Angiogenesis Modeling by Region-Specific Vascular Dynamics
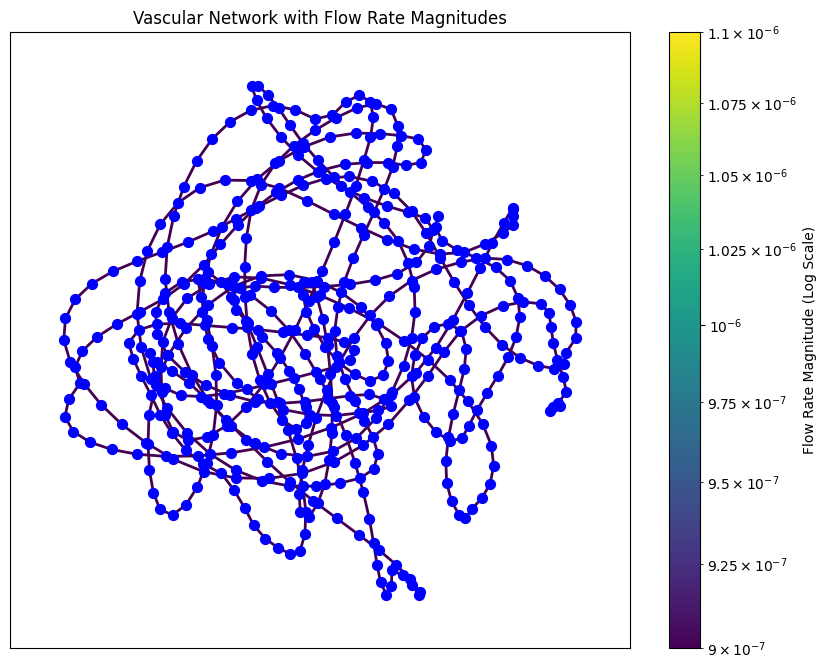
Angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels, is critical for cancer progression and metastasis. This study investigates how location-specific vascular dynamics, such as pressure gradients and flow rates, influence angiogenesis rates. Using computational modeling, vascular networks were simulated for different body regions, including arms or legs, kidneys, and lungs, employing biophysical equations like Hagen-Poiseuille's law. The results show that regions with lower pressure gradients (e.g., lungs and arms/legs) exhibit faster angiogenesis due to hypoxia-driven compensatory mechanisms, while highly perfused regions (e.g., kidneys) demonstrate slower angiogenesis despite higher pressure gradients. These findings highlight that angiogenesis is not solely pressure-driven but influenced by the interplay of hypoxia and vascular regulation. This study provides insights into how tumor location impacts angiogenesis and metastasis, offering a foundation for tailoring anti-angiogenic therapies and advancing our understanding of vascular dynamics in cancer progression.